
Photo: By Rdbickel – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, After crossing over occurs, the cell proceeds into metaphase I. The combinations of genes in the chromosomes are changed due to this process, and the areas where crossing over occurs is essentially random.

DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PROPHASE 1 AND 2 CODE
Another way to think about this is imagining the two chromosomes of each homolog pair oriented parallel to the other chromosome pair, and bits of the genetic code being pulled out one chromosome and stitched into the respective part of the other chromosome. This process of association is referred to as “synapsing” and through this process, the homolog pairs form a larger structure referred to as a “tetrad”.ĭuring synapsis, the two chromosomes of the respective homolog pairs exchange chunks of their DNA strands/swap parts of their genome.
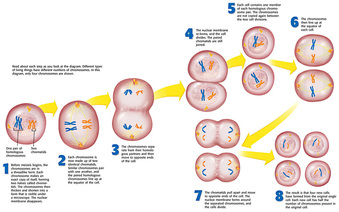
During prophase I, the two members of each homolog pair in a sex cell become linked to one another along the entire length of the chromosome. Throughout most of the meiosis process, ending in metaphase II, the sister chromatids stay attached to one another, bound at the centromere. The spindle fibers eventually extend all the way, moving the centrosomes to opposing ends of the cell, the poles.Įach of the chromosomes found within the cell at this point are made out of two sister chromatids, and these chromatids have genetic information that is identical. The spindle apparatus is created by long spindle fibers that extend from the two centrosomes within the cell. The nucleolus, the smaller organelle within the nucleus, disappears as well. The nuclear envelope, the structure that surrounds the nucleus, breaks up, vanishing. This makes the chromosomes visible under a light microscope. This means that during prophase I, the chromosomes condense, becoming thicker and shorter. What happens during prophase I of meiosis? What Happens During Prophase I?īy the time prophase I of meiosis begins, the chromosomes within the cell have duplicated and prepared for cellular division. However, unlike mitosis, meiosis goes through two round of cellular division, so there is prophase I and prophase II, metaphase I and metaphase II, etc. Meiosis creates daughter cells that possess half as many chromosomes as the parent cell, and meiosis proceeds through four different phases, just like mitosis does: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis is the process that creates new daughter cells from the original parent cells, while meiosisis a similar process that creates just one type of cell – sex cells, or gametes. Prophase II issimilar to prophase in mitosis in that there is thebreak down of the nuclear membrane and the formation of spindlefibers in preparation for the separation of sisterchromatids.The human body needs to create new cells to replace old, worn out ones. The crossing over of homologous chromosomes occurs in prophase I of meiosis. Taking Into Account The Following, Does Crossing Over happen in prophase II? While chromosomeduplication took place prior to meiosis I, no new chromosomereplication occurs before meiosis II. In prophase II, the nuclear envelopebreaks down and the spindle apparatus forms. Meiosis II begins without any further replicationof the chromosomes. You Should Also Know, what happen in prophase 2? The nuclear envelopedisappears at the end of prophase I, allowing thespindle to enter the nucleus. The duplicatedhomologous chromosomes pair, and crossing-over (the physicalexchange of chromosome parts) occurs. Also, what exactly happens during prophase I? During prophase I, they coil and become shorterand thicker and visible under the light microscope. Prophase ? 2:? Prophase ? 2? occurs? in? haploid? cells. Prophase ? 1 :? Prophase ? 1 ? occurs? in? diploid? cells. Prophase ? 2:? Individual? chromosomes? are? involved? in? the? prophase ? 2. Does Crossing Over happen in prophase II?įurthermore, what is the key difference between prophase and prophase 1? Besides, 1 :? Homologous? chromosomes? are? involved? in? the? prophase ? 1.what exactly happens during prophase I?.what is the key difference between prophase and prophase 1?.

What is the difference between prophase 1 and prophase 2? - science Content


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
